REACH with VICTORIA RAY
Step into who you were meant to be!
Get my free guide, “Poise and Potential,” and start confidently showing up as your best self.
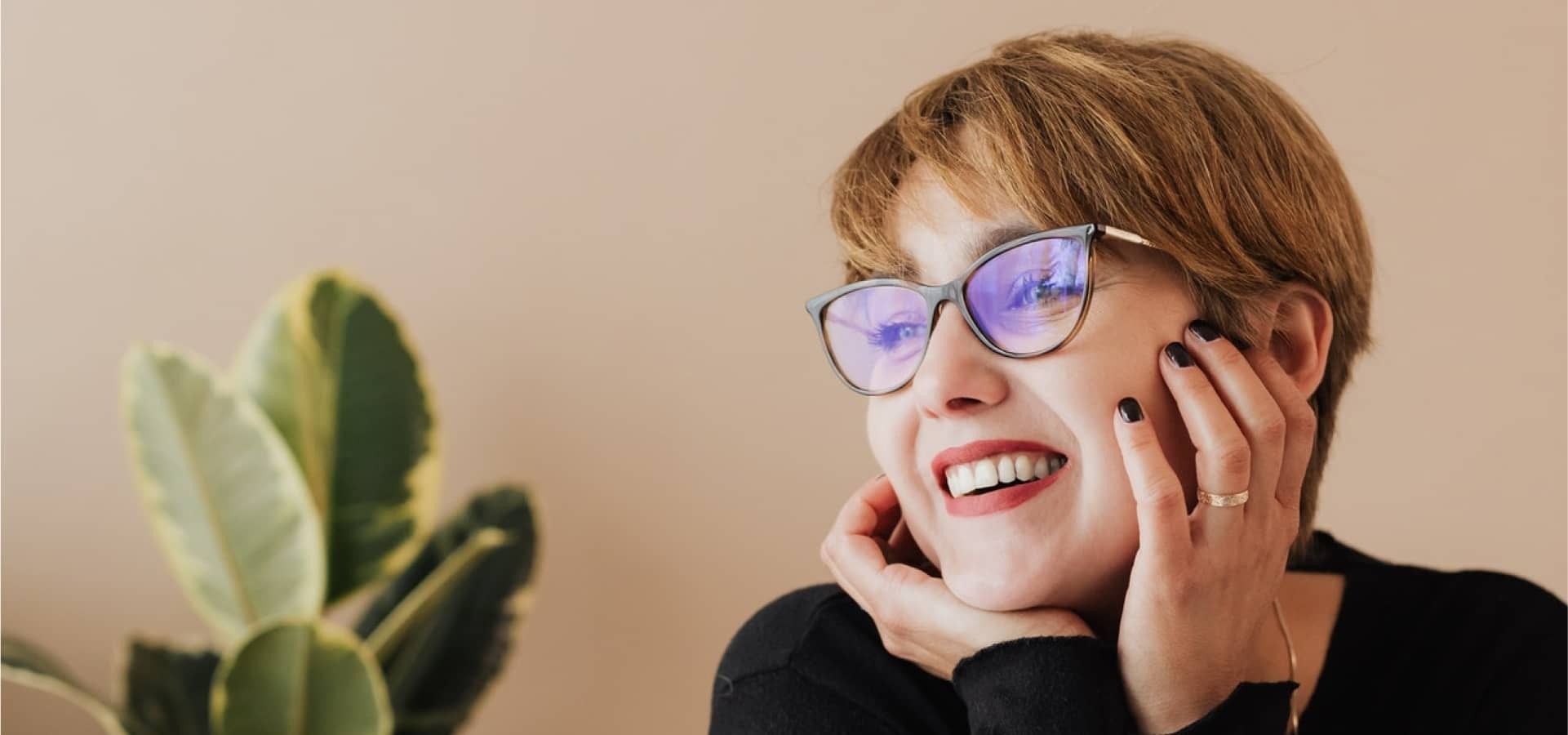
For me, your development is personal!
After struggling to feel comfortable in my own skin for years, I finally decided to do something about it. What started as a quest to conquer my own insecurities has turned into a system that has helped hundreds of my members step into who they really are and confidently show up in their lives like never before.
Read my story

Resources for every stage of the journey

DIY guides
Learn actionable skills you can easily use to improve your daily life.
My life will never be the same and it’s all thanks to Victoria!
Kate Maple
Victoria showed me it was OK to be me and taught me how to love life again.
Rebecca Waters
Get started with one of my 6-week courses

Create good energy
We hear the saying “good vibes only” everywhere, but that’s easier said than done. Good vibes are not about pretending nothing is wrong. They’re about creating positive energy around yourself and what you’re doing.
Start this course
An attitude of gratitude
When you come from a place of abundance and gratitude, your whole life will change. This course will help you appreciate life (even the aspects you used to dread), and you’ll see success and failure from a fresh perspective.

Who you’re meant to be
We are all unique individuals with dreams and desires. As we grow, the world around us begins to influence our identity. This course will lead you on a journey of self-discovery where you step into who you’re meant to be with confidence.
Start the courseStay Connected
Get resources, motivation, and guided activities delivered to your inbox: